RunLoop 相关
简介
基本作用
- 保持程序的持续运行
- 处理APP中的各种事件(比如触摸事件、定时器事件等)
- 节约CPU性能,提高程序性能;该做事时做事,该休息时休息
- .....
RunLoop对象
-
iOS中有2套API来访问和使用RunLoop
- Foundation:NSRunLoop
- Core Foundation:CFRunLoopRef
-
获取当前RunLoop
NSRunLoop *runloop = [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]; // OC CFRunLoopRef runloop2 = CFRunLoopGetCurrent(); // C -
NSRunLoop和CFRunLoopRef都代表着RunLoop对象,NSRunLoop是基于CFRunLoopRef的一层OC包装;
CFRunLoopRef是开源的 :https://opensource.apple.com/tarballs/CF/
RunLoop与线程
- 每条线程都有唯一的一个与之对应的RunLoop对象
- RunLoop保存在一个全局的Dictionary里,线程作为key,RunLoop作为value
- 线程刚创建时并没有RunLoop对象,RunLoop会在第一次获取它时创建
- RunLoop会在线程结束时销毁
- 主线程的RunLoop已经自动获取(创建),子线程默认没有开启RunLoop
获取RunLoop对象
//Foundation
[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]; // 获得当前线程的RunLoop对象
[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop]; // 获得主线程的RunLoop对象
//Core Foundation
CFRunLoopGetCurrent(); // 获得当前线程的RunLoop对象
CFRunLoopGetMain(); // 获得主线程的RunLoop对象
RunLoop相关的类
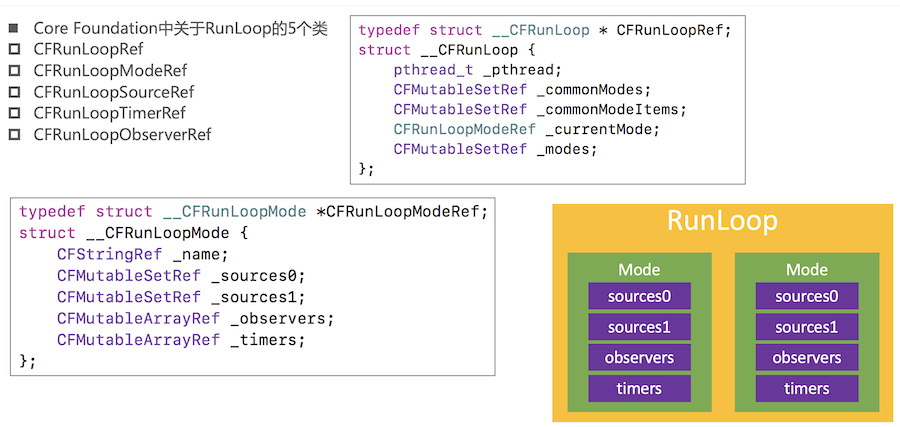
CFRunLoopModeRef
- CFRunLoopModeRef代表RunLoop的运行模式
- 一个RunLoop包含若干个Mode,每个Mode又包含若干个Source0/Source1/Timer/Observer
- RunLoop启动时只能选择其中一个Mode,作为currentMode
- 如果需要切换Mode,只能退出当前Loop,再重新选择一个Mode进入;不同组的Source0/Source1/Timer/Observer能分隔开来,互不影响
- 如果Mode里没有任何Source0/Source1/Timer/Observer,RunLoop会立马退出
- 常见的2种Mode
- kCFRunLoopDefaultMode(NSDefaultRunLoopMode):App的默认Mode,通常主线程是在这个Mode下运行
- UITrackingRunLoopMode:界面跟踪 Mode,用于 ScrollView 追踪触摸滑动,保证界面滑动时不受其他 Mode 影响
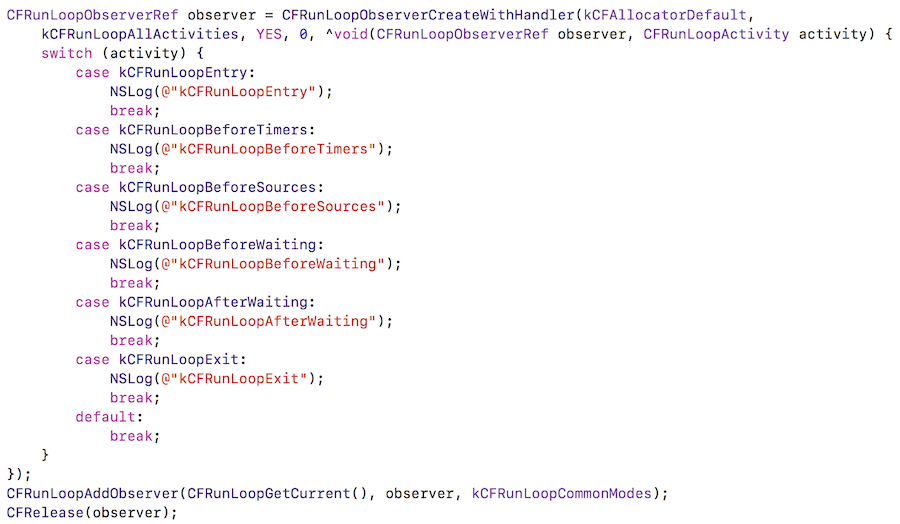
CFRunLoopObserverRef

添加Observer监听RunLoop的所有状态
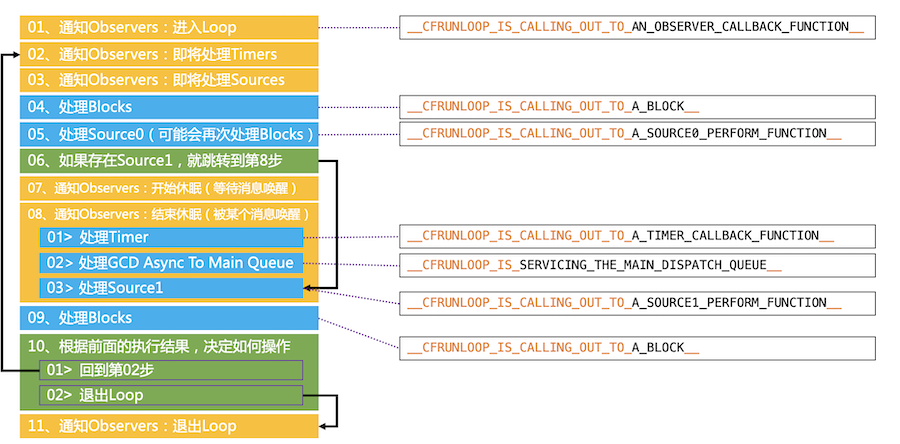
RunLoop的运行逻辑
线程保活
DNPermenantTheread.h
@interface DNPermenantTheread : NSObject
/// 开启线程
- (void)run;
/// 执行任务
/// @param task 任务
- (void)executeTask:(void(^)(void))task;
/// 关闭线程
- (void)stop;
@end
DNPermenantTheread.m
#import "DNPermenantTheread.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@interface DNPermenantTheread()
@property (nonatomic, assign, getter=isStopped) BOOL stopped;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSThread *innerThread;
@end
@implementation DNPermenantTheread
- (instancetype)init{
if (self = [super init]) {
self.stopped = NO;
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
self.innerThread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithBlock:^{
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addPort:[[NSPort alloc]init] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
while (weakSelf && !weakSelf.isStopped) {
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate: [NSDate distantFuture]];
}
}];
}
return self;
}
#pragma mark - public methods
- (void)run{
if (!_innerThread) return;
[self.innerThread start];
}
- (void)executeTask:(void(^)(void))task{
if (!_innerThread || !task) return;
[self performSelector:@selector(__executeTask:) onThread:self.innerThread withObject:task waitUntilDone:NO];
}
- (void)stop{
if (!_innerThread) return;
[self performSelector:@selector(__stop) onThread:self.innerThread withObject:nil waitUntilDone:YES];
}
#pragma mark - private methods
- (void)__stop{
self.stopped = YES;
CFRunLoopStop(CFRunLoopGetCurrent());
}
- (void)__executeTask:(void(^)(void))task{
task();
}
@end
阅读量
loading...